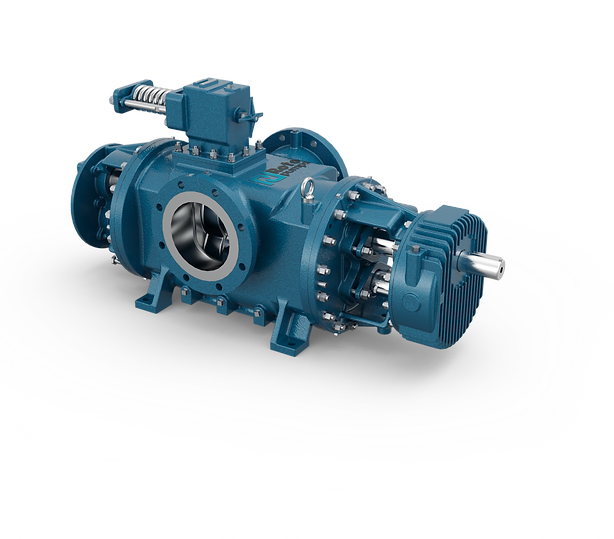
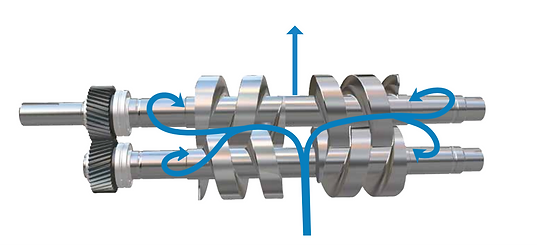
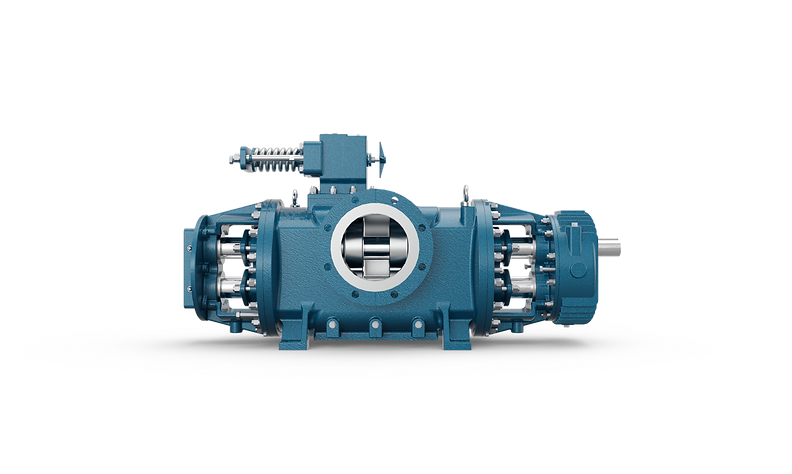
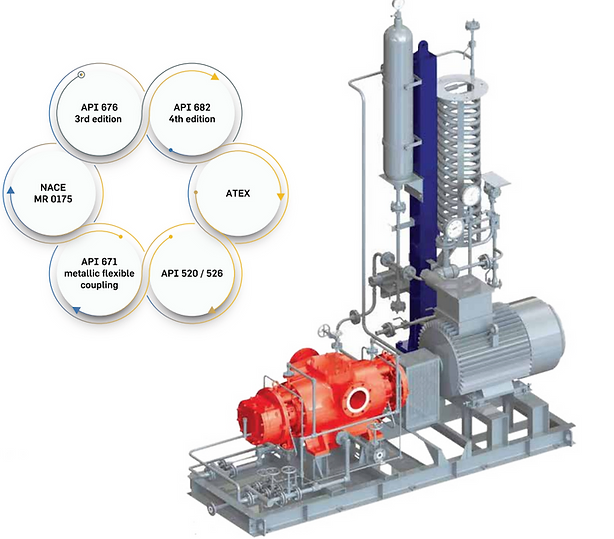
- HOME
- MARKETS
- Our products
-
-
- PUMPS
- EKSENTERSKRUEPUMPER
- PERISTALTISKE PUMPS
- DOSAGE PERISTALTISKE PUMPS
- PUMPS
- LOBEPUMPER – DRAIN/INDUSTRY
- DOSAGE – PISTON PUMPS
- DOSAGE – DIAPHRAGM PUMPS
- AIR DRIVEN DIAPHRAGM PUMPS
- DRAIN – SELVSUGENDEPUMPER
- DRAIN – SKRUESENTRIFUGALPUMPER
- GRUNNVANNSPUMPER
- MAGNETDREVNE PUMPS
- WATER supply
- VORTEX PUMPS
- VÆSKERINGSVAKUUMPUMPER
- FATPUMPER
- MULTI-STAGE CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS
- EKSENTERS DISKPUMPE/TETNINGSFRI
- SIDEKANALBLÅSERE
- Centrifugal pumps
- VINGEPUMPER – MAG DRIVE PUMP
- CENTRIFUGAL MAG DRIVE
- HCM – CENTRIFUGAL MAG DRIVE
- PERIFERISKE AND GEAR PUMPS
- MAG-M CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS
- REGENERATIVE TURBINE PUMP
- CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS-FOOD
- SEALS
- CHOPPER PUMPS – PS SERIES
- FILTER
- PUMPS
-
-
- Pumping stations
- Online shop
- ABOUT US
- CONTACT